Endocarditis infective, libman sacks causes, symptoms, treatment & pathology YouTube

PDF | On Apr 1, 2017, Nerea Gómez-Larrambe and others published Libman-Sacks' endocarditis: A frequently unnoticed complication | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
LibmanSacks endocarditis in a male patient with systemic lupus erythematosus ABC Imaging

We concluded the diagnosis was most likely to be non-infective endocarditis—commonly known as Libman-Sacks endocarditis. Laboratory investigations supported this diagnosis: a lupus anticoagulant test was positive and the levels of anticardiolipin IgM and anti-β2 glycoprotein I IgG antibodies—markers of the antiphospholipid syndrome—were.
Cardiac MRI clinches diagnosis of LibmanSacks endocarditis The Lancet

Epidemiology. Data for Libman-Sacks endocarditis comes from several case-controlled studies and cohort studies of patients with SLE. The prevalence of Libman-Sacks endocarditis in one prospective cohort study was estimated by transthoracic echocardiogram at around 11% 1.. However, on post-mortem findings in older studies performed between 1950-1960 identified rates were as high as 35-65% of.
(PDF) Un caso de endocarditis de Libman Sacks

Libman-Sacks endocarditis is a distinctive heart manifestation in the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus [ 1, 3 ]. However, it is rare in the pediatric age group with not enough evidence about the management [ 2, 4 ]. SLE can present as pericarditis, arrhythmias, abnormal conduction, myocarditis, and increased pulmonary pressure [ 1, 2 ].
(PDF) LibmanSacks endocarditis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with secondary

LS endocarditis was a phenomenon first described in 1924 by Emanuel Libman and Benjamin Sacks, in which they characterized non-bacterial verrucous valvular disease in four patients with SLE [].Over the years, the presence of LS endocarditis has been reported numerous times in the literature, particularly describing significant valvular insufficiency requiring surgical intervention.
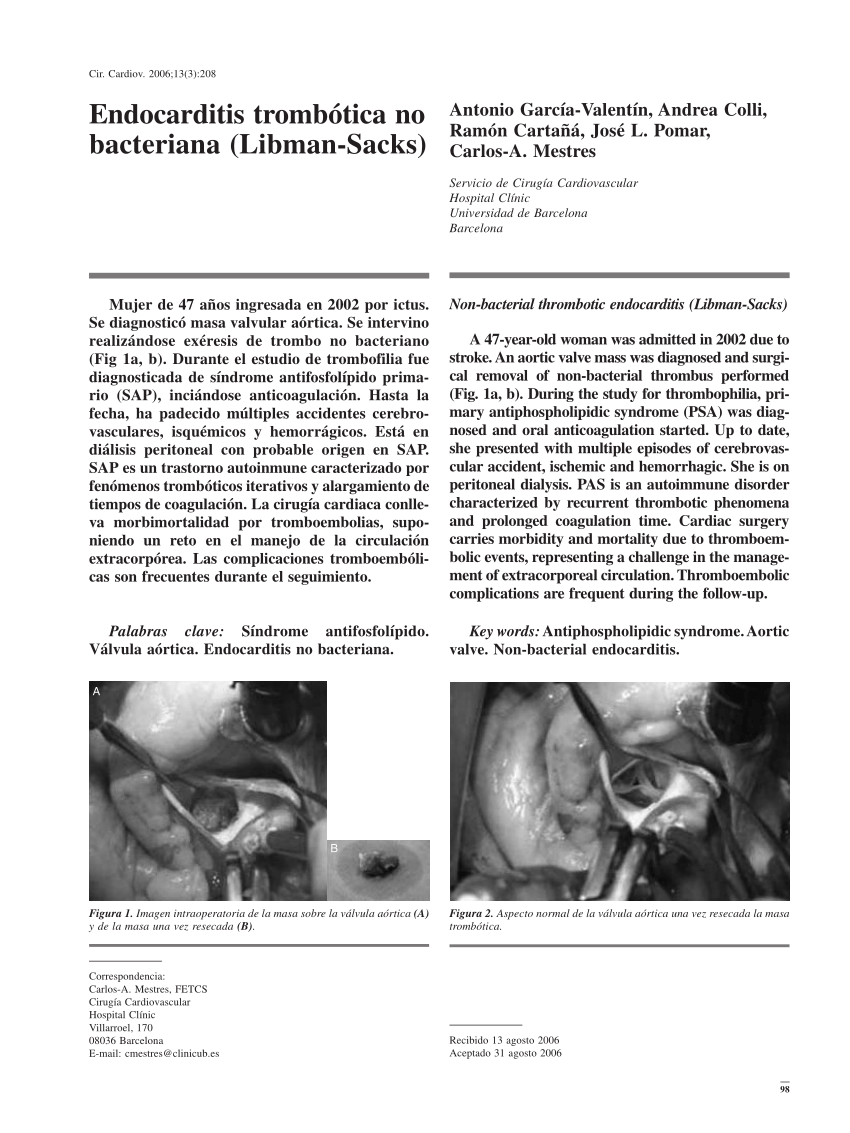
(PDF) Endocarditis trombótica no bacteriana (LibmanSacks)
Libman-Sacks endocarditis is a rare disease that mostly found postmortem with a prevalence of about 0.9 % to 1.6%. LB endocarditis most commonly affects patients between 40 to 80 years of age, although it can occur in every age group. Studies do not show any sex predilection. However, SLE and antiphospholipid show a predominance in women of.
(PDF) Estenosis aórtica severa secundaria a endocarditis de LibmanSacks

Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Libman-Sacks endocarditis versus infectious endocarditis" by I. Porubčinová et al. Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu. Semantic Scholar's Logo. Search 217,798,474 papers from all fields of science. Search. Sign.
(PDF) P1702 LibmanSacks endocarditis of the mitral valve combined with right atrial thrombus

The case of isolated mitral regurgitation with abnormal looking mitral valve, detected in early childhood, which deteriorated to a severe degree in the next decade and was diagnosed as Libman-Sacks endocarditis after surgical repair from histopathology is presented.
(PDF) Endocarditis de LibmanSacks de válvulas nativas derechas en contexto de síndrome

L'endocardite de Libman-Sacks (ELS), également connue sous le nom d'endocardite verruqueuse atypique, est une manifestation cardiaque bien connue du lupus érythémateux disséminé, trouvée.
ENDOCARDITIS DE LIBMAN SACKS PDF

Background: Libman-Sacks endocarditis, characterized by Libman-Sacks vegetations, is common in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and is commonly complicated with embolic cerebrovascular disease. Thus, accurate detection of Libman-Sacks vegetations may lead to early therapy and prevention of their associated complications.
(PDF) Endocarditis de LibmanSacks Ana Munera Academia.edu

Abstract Libman-Sacks (LS) endocarditis was first de-scribed by Libman and Sacks in 1924, and is characterized by sterile, verrucous valvular lesions with a predisposition for. Libman-Sacks (LS) endocarditis is a well-known cardiac manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in which sterile valvular vegetations, or masses, are.
[PDF] LibmanSacks endocarditis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with secondary

INTRODUCTION: Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE), "marantic", or "Libman-Sacks" endocarditis is a rare entity describing endocarditis that is non-infectious and usually secondary to advanced malignancy, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), or anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome. NBTE usually is found on autopsy, however some patients are diagnosed antemortem.
21yearold female with LibmanSacks Endocarditis complicated with... Download Scientific Diagram

La endocarditis de Libman y Sacks se caracteriza por vegetaciones estériles valvulares de predominio en las válvulas mitral y aórtica. Su prevalencia es de 53 a 74 %. Se asocia con actividad lúpica y presencia de anticuerpos antifosfolípido. La ecocardiografía, en especial la transtorácica, es el estudio de elección para el diagnós.
(PDF) LibmanSacks Endocarditis and Infective Endocarditis Vegetations Coexisting in a Patient

Libman-Sacks endocarditis, characterized by Libman-Sacks vegetations, is common in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and is commonly complicated with embolic cerebrovascular disease. Thus, accurate detection of Libman-Sacks vegetations may lead to early therapy and prevention of their associated complications.
LibmanSacks Endocarditis Detection, Characterization, and Clinical Correlates by Three

Libman-Sacks endocarditis, best characterized by Libman-Sacks vegetations, is common in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Libman-Sacks vegetations are sterile abnormal growths of tissue around the heart valves with an autoimmune-mediated inflamma-tory and thrombotic pathogenesis.1-4 Libman-Sacks vegetations
Severe Mitral Regurgitation in LibmanSacks Endocarditis. Conservative Surgery Revista
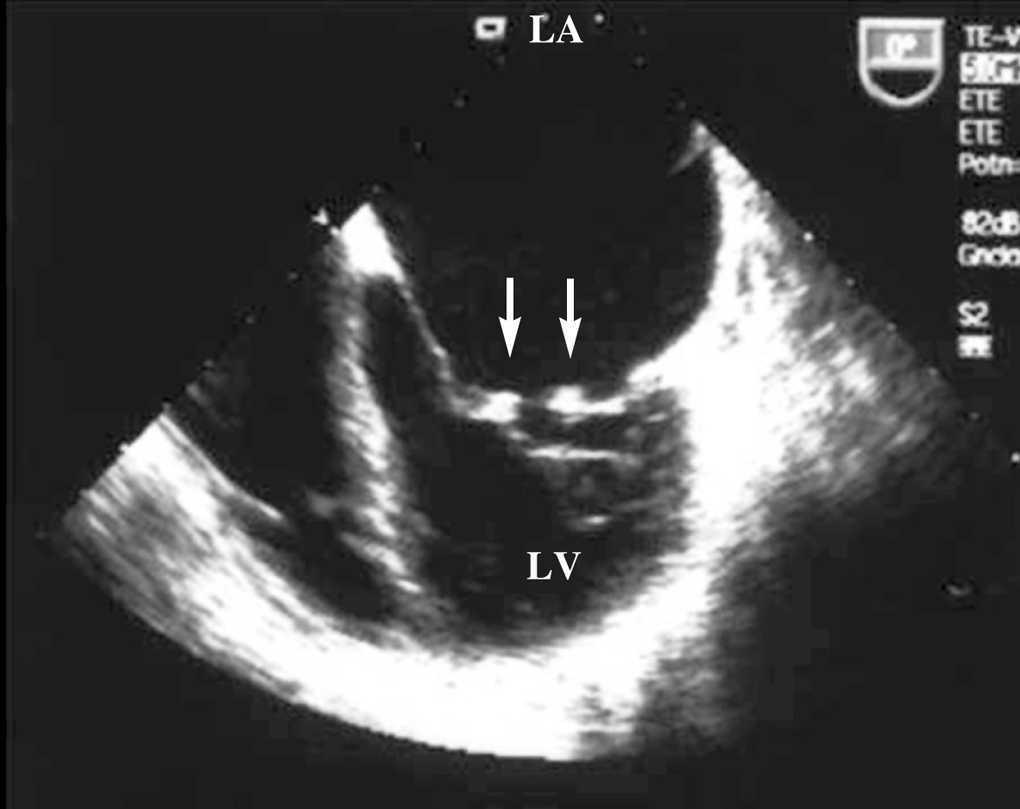
Libman-Sacks endocarditis is a rare condition that can be missed easily as in this case. It can present with severe cardiac manifestation which should be recognized and differentiated from infective endocarditis as the former needs appropriate and timely immunosuppression which may worsen the latter condition.
.