PPT Enzymology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1794432

vibration or a translation over the transition state region. 3. The origins of the kinetic isotope effect. Section B 1. Theoretical expressions for the rate constant, k2, of a bimolecular elementary reaction step include the Eyring equation from transition state theory; k2 = kBT h K ‡ and the collision theory result k2 = P 8 kBT
PPT Chemical the rates of reactions PowerPoint Presentation ID1523033

The Eyring Equation, developed by Henry Eyring in 1935, is based on transition state theory and is used to describe the relationship between reaction rate and temperature. It is similar to the Arrhenius Equation, which also describes the temperature dependence of reaction rates. However, whereas Arrhenius Equation can be applied only to gas.
Thermodynamic Interpretation of Transition State Theory The Eyring Equation YouTube

The theory assumes that reactants are hard spheres rather than molecules with specific structures. In 1935, Henry Eyring helped develop a new theory called the transition state theory to provide a more accurate alternative to the previously used Arrhenius equation and the collision theory. The Eyring equation involves the statistical frequency.
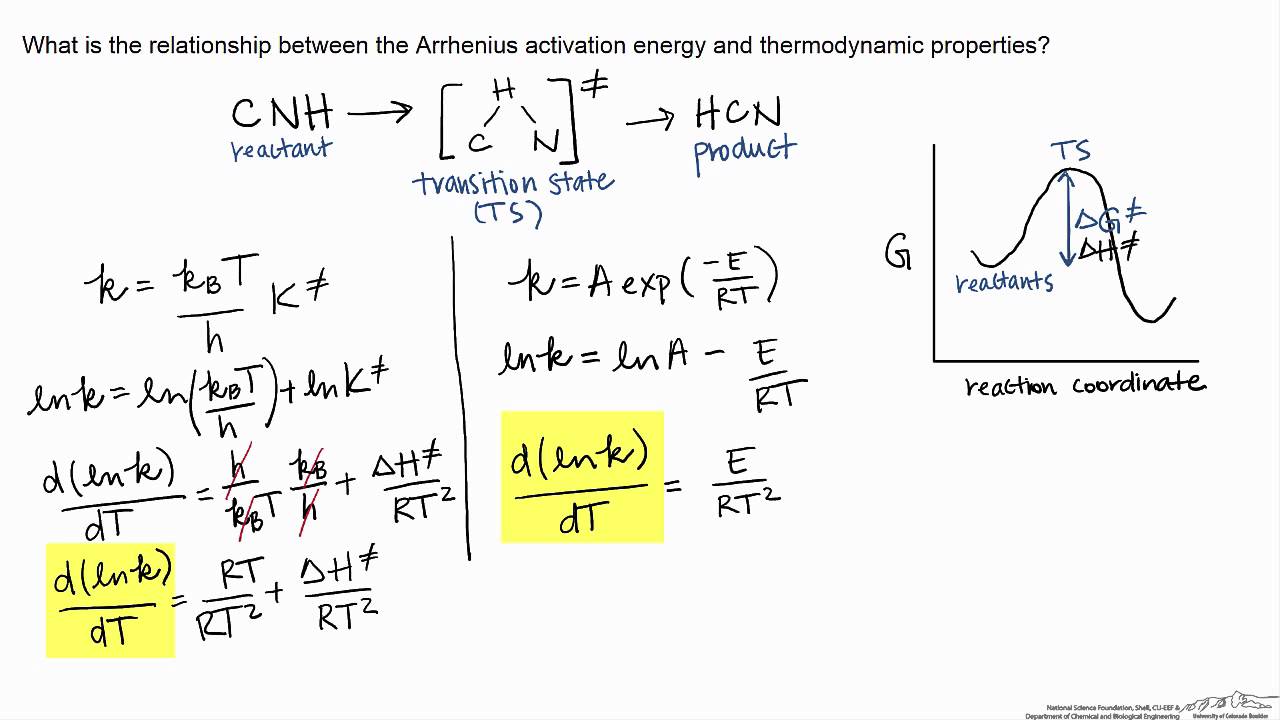
Relationship Between Arrhenius Activation Energy and Transition State Theory (Eyring Equation
California State University East Bay. Transition state theory was proposed in 1935 by Henry Erying, and further developed by Merrideth G. Evans and Michael Polanyi (Laidler & King, 1983), as another means of accounting for chemical reaction rates. It is based on the idea that a molecular collision that leads to reaction must pass through an.
Activated complex theory/ Transition state theory/ Eyring equation YouTube

Using the Eyring equation,. Transition state theory is also based on the assumption that atomic nuclei behave according to classical mechanics. It is assumed that unless atoms or molecules collide with enough energy to form the transition structure, then the reaction does not occur. However, according to quantum mechanics, for any barrier.
PPT Chapter 14 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4450666

Transition state theory relies on three key assumptions in its derivation. Reactants are in constant equilibrium with the transition state structure. The energy of the particles follow a Boltzmann distribution.. The Eyring equation can also be expressed in terms thermodynamic parameters.
PPT Chemical the rates of reactions PowerPoint Presentation ID1523033
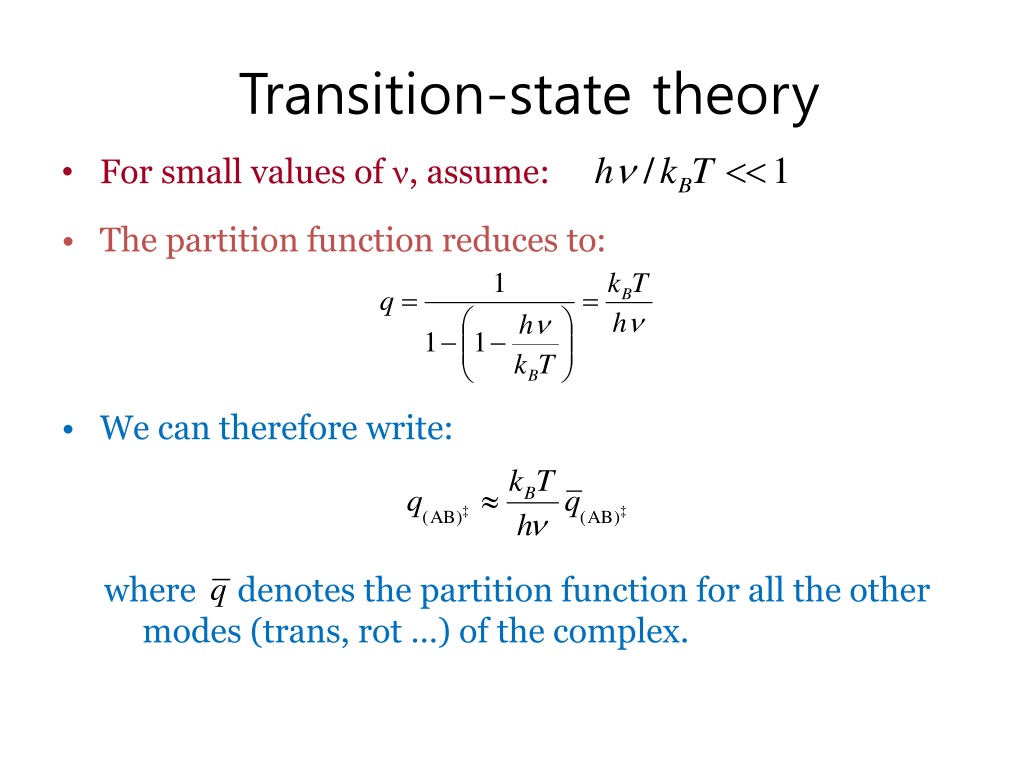
Organized by textbook: https://learncheme.com/Introduces how rate constants can be calculated from thermodynamic properties of transition states. Made by fa.
PPT Chemical the rates of reactions PowerPoint Presentation ID1523033

K ‡ eq = q ‡ / V qR / Ve − Ef a / kBT. Then we write the forward flux in eq. (23.1) proportional to the population of activated complex. J ‡ = v[RP ‡] = vK ‡ eq[R] Here ν is the reaction frequency, which is the inverse of the transition state lifetime τmol. v − 1 or τmol reflects the time it takes to cross the transition state.
Transition State Theory Enthalpy YouTube

This equation is sometimes known as the Eyring equation. The main difficulty in applying transition state theory lies in determining qAB‡. However, modern methods and educated guesswork on the nature of the activated complex AB‡ usually allow rate constants for bimolecular reactions to be estimated to within a factor of two using this.
Get Transition State Theory Equation Ariana
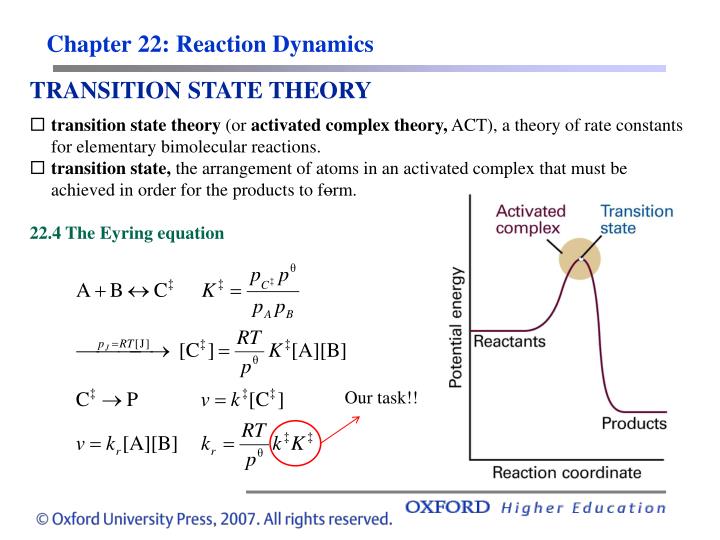
Eyring used the term "activated complex" rather than "transition state" in setting out his theory, using the symbol M ‡ for the activated complex. In fact, he meant to use the traditional transition-state symbol M* as the symbol for the activated complex, but his secretary mistyped it, and a new symbol was born.
Eyring equation transition state theory eyring equation in chemical equation

Transition State Theory: The Eyring Equation G RT h k T k B / rxn = e−Δ ‡ S R H RT h k T k B / / rxn = eΔ ‡ e−Δ ‡ ΔG‡ = ΔH‡ -TΔS‡, so Eyring equation. Relates rate constant to T in a physical way. ΔH‡: Enthalpy required to reach transition state (like E a) ΔS‡: Entropy lost/gained getting to transition state
PPT EXPERIMENT 9 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1769598
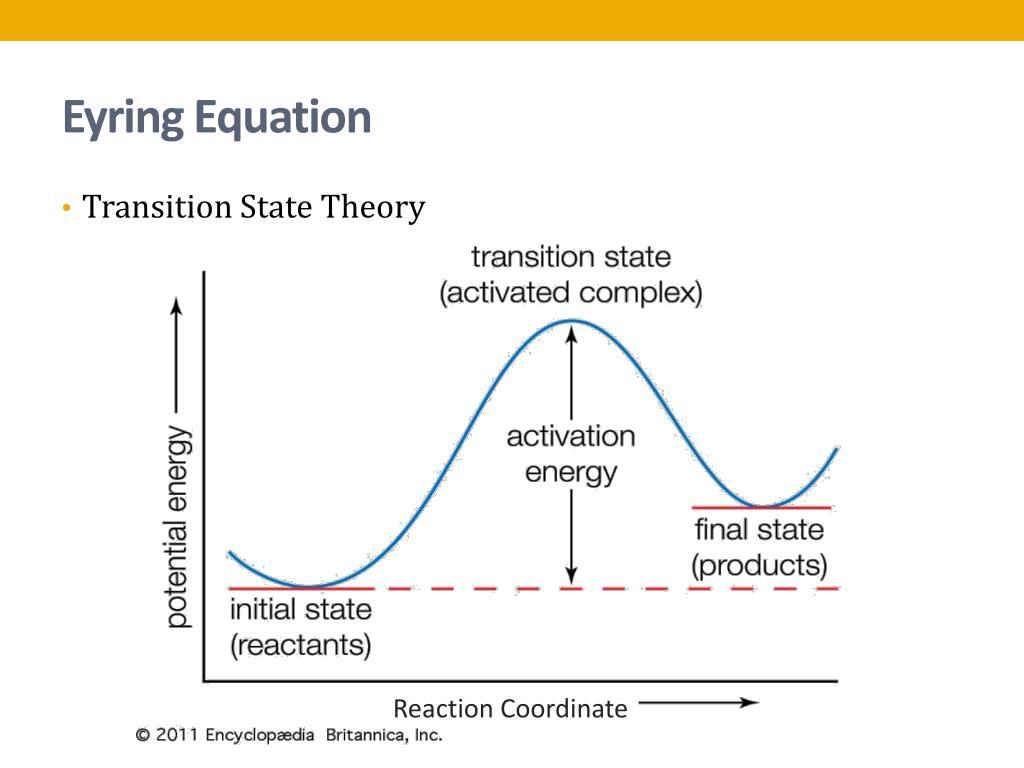
The transition state theory (TST), which is also known as theory of absolute reaction rates (ART) and the theory of activated state (complex), is essentially a refined version of crude collision theory, which treats the reacting molecules as the rigid spheres without any internal degree of freedom. The theory explains the rate of chemical reaction assuming a special type of chemical.
Get Transition State Theory Equation Ariana
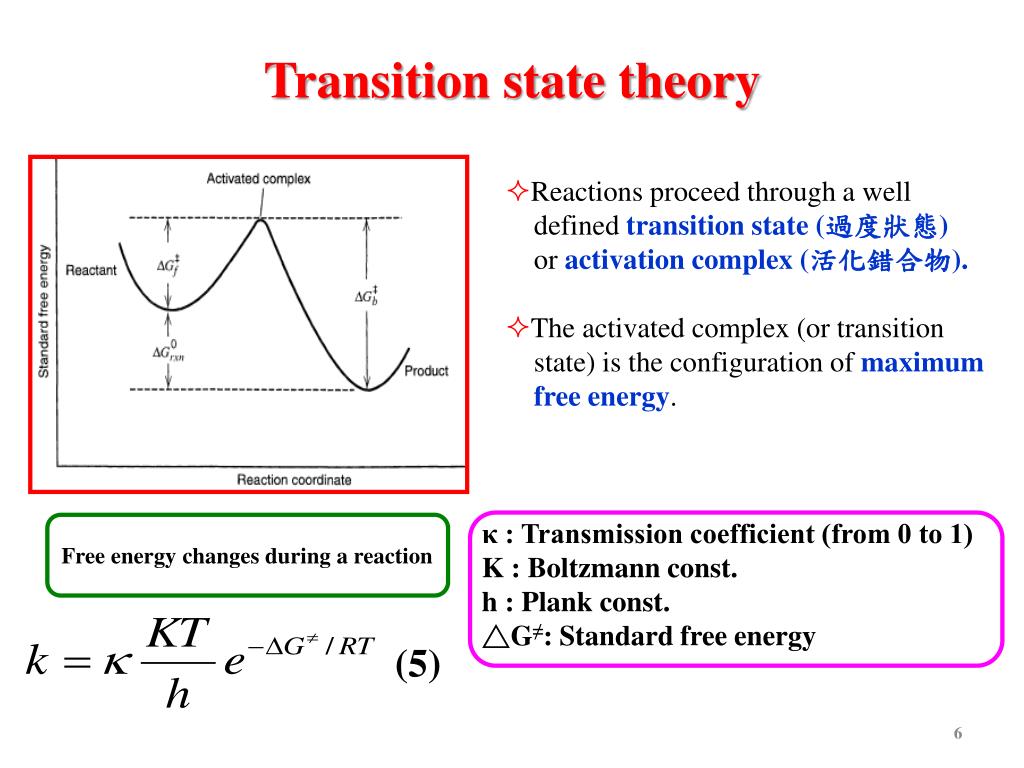
The Eyring equation (occasionally also known as Eyring-Polanyi equation) is an equation used in chemical kinetics to describe changes in the rate of a chemical reaction against temperature.It was developed almost simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi.The equation follows from the transition state theory, also known as activated-complex theory.
Eyring analysis of transitionstate thermodynamics Linear Eyring plots... Download Scientific

In transition state theory (TST) an activated molecule is formed during the reaction at the transition state between forming products from reactants.. The Eyring Equation Liquids Gases R. I. Masel, Chemical Kinetics and Catalysis, Wiley Interscience, New York, 2001. References Nomenclature. A5p403 Means Atkins, P. W. Physical Chemistry, 5th.
14.5 Transition State Theory YouTube

Since its establishment in 1949, and with growing popularity in recent years, Eyring's transition-state theory (TST) for transmembrane permeation has been applied in numerous studies to mechanistically explore molecular transport in membranes including RO and NF. In this review, we critically assess TST applied to transmembrane permeation in.
TRANSITION STATE THEORY ACTIVATED COMPLEX THEORY EYRING EQUATION CHEMICAL YouTube

(i) Transition state theory. The Eyring formulation [4,6] of chemical reaction rates provided chemists with the basic ingredients for understanding and even predicting both parameters A and E of the Arrhenius equation (equation (2.9)) and is assumed as a paradigm for describing the temperature dependence of the rate coefficient of chemical.
.

